Submit
Submit feedback
Key Considerations When Choosing Forged Wheels In Vehicle Modification
2025-11-14
Aluminum alloy wheel factory are vital hubs in the modern automotive industry, combining advanced materials science with precision engineering. These facilities focus on designing and producing wheels that offer lightweight performance, high durability, and aesthetic appeal. The core advantages of aluminum alloy wheels—better heat dissipation, enhanced handling, and fuel efficiency—continue to drive demand in both OEM supply and the aftermarket modification sector.

Key Capabilities of a Modern Alloy Wheel Factory
Material Control — Utilization of high-strength aluminum alloy grades ensures better density and load-bearing capacity.
- Multiple Manufacturing Methods
- Low-pressure casting for cost-effective mass production
- Flow forming for improved structural integrity
- Forging for premium performance wheels
Automated CNC Machining — Enhances precision in spoke design, weight reduction pockets, and fitment compatibility.
Quality Assurance Processes
- X-ray internal structure inspection
- Radial fatigue and impact tests
- Balancing and surface coating durability tests
Surface Treatment & Custom Finishes — Powder coating, anodizing, diamond cutting, brushing, or multi-tone painting.
A competitive aluminum alloy wheel factory not only invests in advanced equipment but also emphasizes engineering innovation and strict compliance with safety standards such as JWL, VIA, TUV, and SAE.
Key Considerations When Choosing Forged Wheels
Forged wheels are premium upgrades that improve performance, aesthetics, and vehicle safety. When selecting forged wheels—whether for personal use, motorsports, or commercial distribution—these critical considerations should be evaluated:
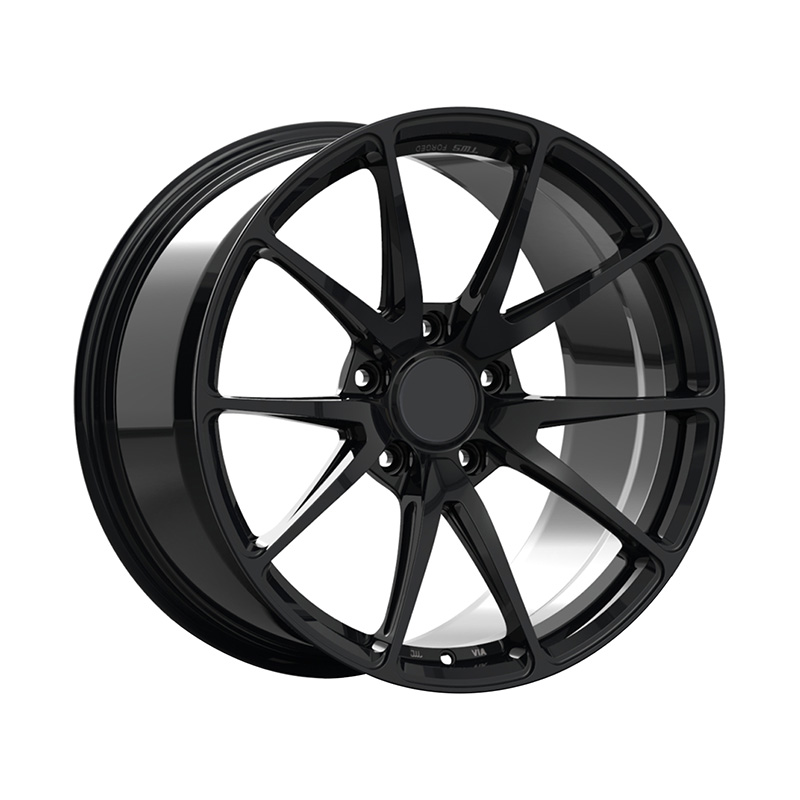
1. Manufacturing Process & Forging Grade
Look for fully forged (monoblock or multi-piece) rather than simple flow-formed or cast alternatives marketed as forged.
The forging press tonnage matters — 6,000–10,000 tons is typical for high-performance wheels.
Controlled grain flow = higher impact resistance and fatigue life.
2. Wheel Fitment Accuracy
Improper fitment leads to handling issues and even safety risks.
Confirm diameter, width, offset (ET), bolt pattern (PCD), hub bore, and brake caliper clearance.
Ask for measurement consultation if installing big brake kits or wide-body modifications.
3. Weight vs. Strength
A balanced design ensures lower unsprung mass without compromising load capability.
Request weight specs to compare against standard cast wheels.
4. Material Grade & Certification
Preferred materials: 6061-T6 aviation-grade aluminum.
Ensure certification compliance:
SAE, ISO, TUV, JWL/VIA for global market approval.
5. Design Customization
Consider spoke design, concavity profile, color finishing, and branded center caps.
Multi-piece forged wheels offer modular styling flexibility but require more maintenance.
6. Application Scenario
Choose based on intended driving conditions:
|
Use Case |
Best Choice |
Benefit |
|
Track / Racing |
Lightweight monoblock forged |
Strength + agility |
|
Daily street / SUV |
Reinforced multi-spoke designs |
Load capacity + durability |
|
Luxury show cars |
Deep concave / multi-piece |
Strong visual impact |
7. Manufacturer Experience & After-Sales Support
Select a reputable factory capable of engineering drawings, simulation analysis, and sample testing.
After-sales service for refinishing or repairs adds long-term value.
A Comparison Of Forged vs. Cast vs. Flow-Formed Wheels In Car Modification
Forged vs. Cast vs. Flow-Formed Wheels
Forged Wheels — Performance Priority
Forged wheels are made by applying extreme pressure to a solid aluminum billet, creating a dense and extremely strong structure.
Advantages
- Outstanding strength-to-weight ratio
- Better acceleration, braking, and handling due to lower rotational mass
- Excellent durability for high-horsepower and motorsport use
- Superior resistance to cracks and deformation
Drawbacks
- Highest cost due to advanced equipment and machining
- Longer production lead time for full customization
Suitable for: Performance builds, track-focused cars, supercars, modified EVs with heavy loads
Cast Wheels — Budget-Friendly and Widely Available
Cast wheels are produced by pouring molten aluminum into a mold, shaping the wheel economically for mass production.
Advantages
- Most affordable option
- Many designs available in retail markets
- Suitable for daily driving
Drawbacks
- Weaker structure from air pockets in casting
- Heavier weight impacts fuel efficiency and handling
- More prone to cracking under strong impact
Suitable for: Stock replacements, visual upgrades on budget-conscious builds
Flow-Formed Wheels — The Balanced Middle Ground
Flow-formed wheels begin as cast, then undergo barrel stretching with high-pressure rollers, enhancing metal density similar to forging.
Advantages
- Lighter and stronger than cast wheels
- More affordable than forged wheels
- Good compromise for spirited driving
Drawbacks
- Strength mainly improved in the rim barrel; spokes are still cast
- Not as durable or customizable as forged wheels
Suitable for: Street performance enthusiasts seeking value and lightweight benefits
recommend products
-
Zhenlun Multi Spokes Split Monoblock Forged Wheels Bronze With Silver Lip Edge
-
Zhenlun Matt Black With Red Lip Monoblock Forged Wheels
-
Zhenlun Gloss Black Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black For Sports Car
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Lightgrey With Machined Face
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black Dense Multi Spoke

 0
0