Submit
Submit feedback
Modification of Forged Wheels for Different Models of Cars and SUV
2025-06-13
Forged wheels factory have become a popular choice among car and SUV enthusiasts due to their strength, lightweight properties, and aesthetic appeal. Modifying forged wheels for different models of cars and SUV involves a combination of engineering precision and design adaptability. Whether it's for aesthetic customization, performance enhancement, or fitment adjustments, modifying forged wheels requires a deep understanding of the vehicle's specifications and the intended use of the wheels.

Why Modify Forged Wheels?
Performance Improvements: Lighter wheels reduce unsprung mass, which enhances acceleration, braking, and handling. Forged wheels modified for optimal weight and strength distribution can significantly improve a vehicle's performance on both road and track.
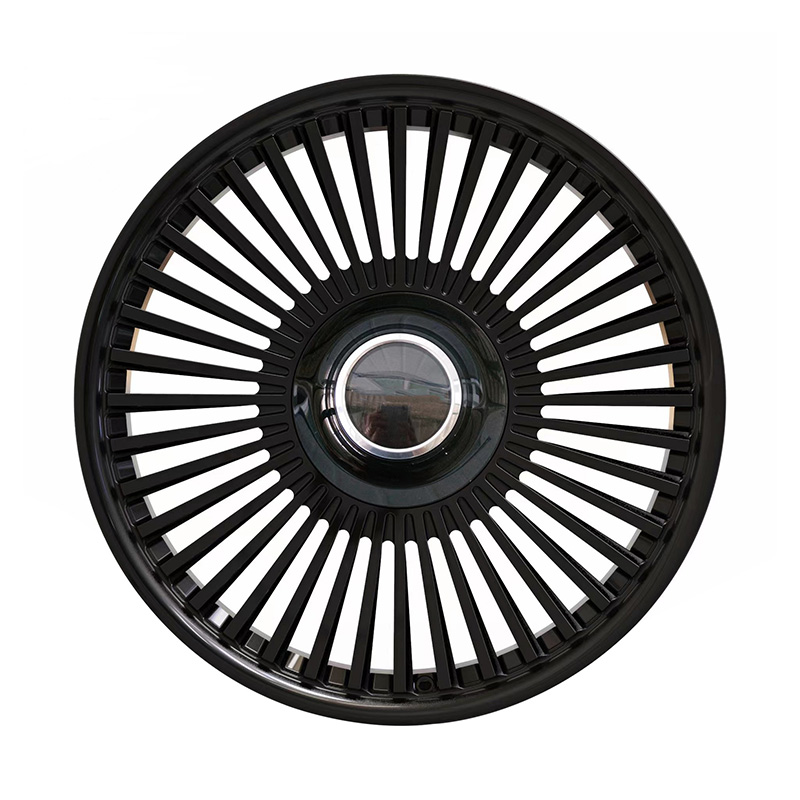
Aesthetic Customization: Owners often modify wheels to personalize the look of their vehicles. Forged wheels are ideal for customization because they can be machined into various shapes, finishes, and colors to match the owner's style or brand image.
Fitment Requirements: Every car or SUV model has unique bolt patterns, offsets, and hub sizes. Modifying forged wheels ensures that they properly fit the target vehicle, avoiding issues such as rubbing, poor alignment, or safety hazards.
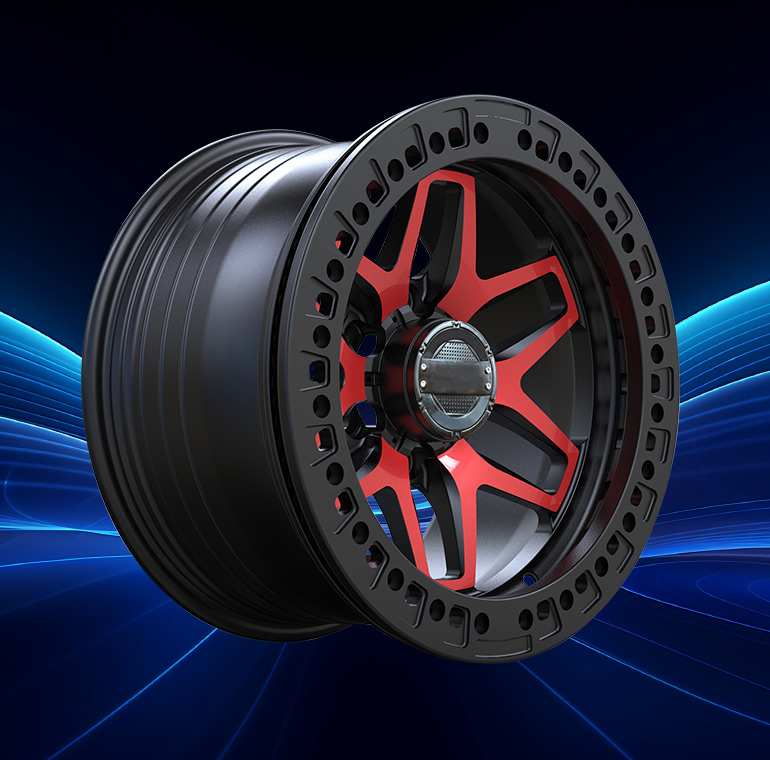
Off-Road Adaptation for SUV: For off-road SUV, forged wheels may be modified to increase strength in high-impact environments, accommodate larger tires, and ensure durability under extreme conditions.

Key Aspects of Forged Wheel Modification
1. Bolt Pattern Customization
The bolt pattern refers to the arrangement of lug holes on a wheel and must match the vehicle's hub. Different models and manufacturers use different bolt patterns (e.g., 5x114.3, 6x139.7). Modifying forged wheels to change or fine-tune the bolt pattern ensures compatibility and safe mounting.
2. Offset and Backspacing Adjustments
Offset (positive, negative, or zero) affects how far the wheel sticks out from the hub. It must be adjusted correctly to avoid clearance issues with fenders or suspension components. Custom forged wheels can be machined with precise offsets to suit the vehicle's geometry.
3. Center Bore Modification
The center bore must match the vehicle's hub to ensure the wheel is hub-centric, which improves stability and reduces vibrations. Forged wheels can be drilled or machined to adjust the bore size for a perfect fit.
4. Load Rating Considerations
SUV, especially those used for towing or off-roading, require wheels with a higher load rating. Modifying forged wheels for these vehicles often involves reinforcing the design and using stronger materials to meet or exceed the required specifications.
5. Design Customization
With CNC machining, forged wheels can be designed with intricate spokes, custom engravings, and various surface finishes such as brushed, polished, powder-coated, or anodized. This allows for nearly endless personalization options.
Vehicle-Specific Modifications
Sports Cars: Forged wheels for sports cars are often modified for lightweight performance and aerodynamic design. Wider wheels with staggered setups (wider rear wheels than front) are common for improved traction and handling.
Luxury Sedans: For these vehicles, aesthetic appeal and ride comfort are priorities. Forged wheels are modified with stylish finishes and optimized for smooth rides rather than aggressive performance.
SUV and Trucks: Forged wheels for these vehicles emphasize strength, high load capacity, and rugged design. Beadlock compatibility may be added for off-road purposes, and custom sizes are used to accommodate larger tires.
recommend products
-
Zhenlun Multi Spokes Split Monoblock Forged Wheels Bronze With Silver Lip Edge
-
Zhenlun Matt Black With Red Lip Monoblock Forged Wheels
-
Zhenlun Gloss Black Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black For Sports Car
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Lightgrey With Machined Face
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black Dense Multi Spoke

 0
0